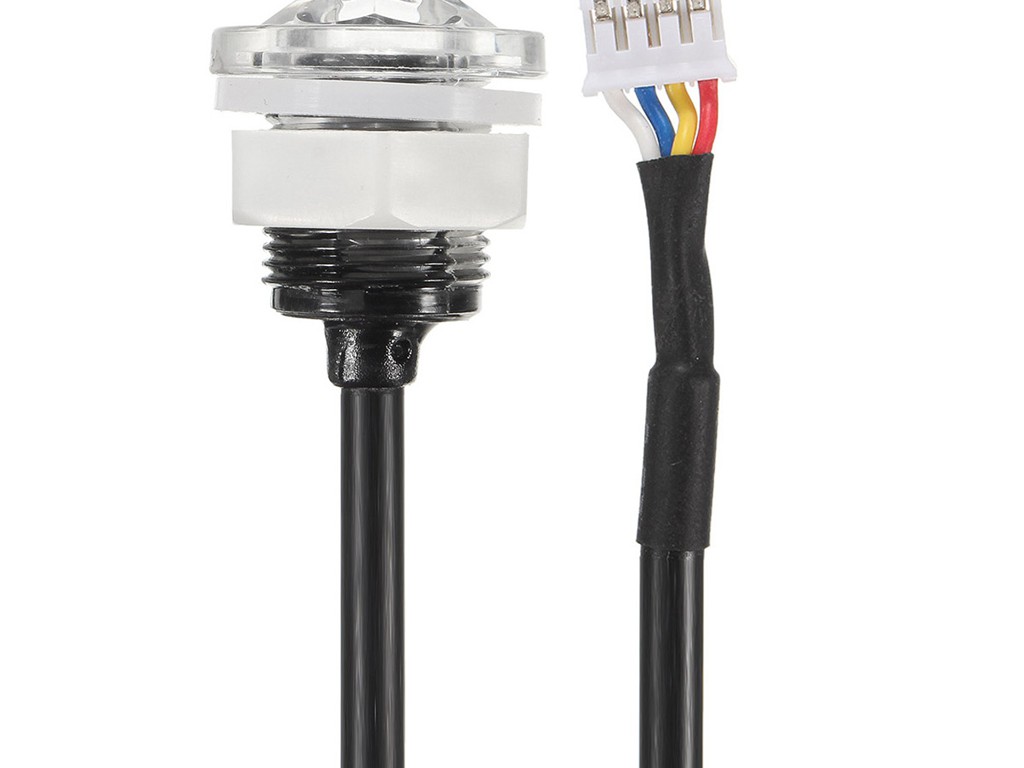
T30 Liquid Level Detection Sensor
The T30 Liquid Level Detection Sensor to detect liquids. The resulting signal is transmitted optically and then converted to an electrical output. This voltage signal is collected and used for level discrimination. The design of the sensor offers many benefits, such as being compact, small, waterproof, cylindrical, square, and suitable for drilling installation. The installation method allows for stacking and can be done vertically, horizontally or at an angle. Additionally, the smooth sensor head can be easily cleaned and offers better accuracy (within 0.5mm) compared to traditional float type liquid level switches which only have an accuracy of 3.0mm due to their use of mechanical parts. As a result of using infrared rays, T30 Liquid Level Detection Sensor requires no friction or moving parts, greatly increasing its lifespan.
- The technical parameters that need to be considered are numerous. It is essential to take into account various technical aspects.
- The working voltage can be adjusted to meet special requirements, ranging from DC5V to 12V/24V.
- Current consumption: <10mA
- Output modes: Analog output 0-4.5V, High/low level signal output
- Response time: <500ms
- Insulation resistance: 100M
- Operating temperature: -30 to 80 degrees Celsius
- Operating humidity: 0-100% RH
- Waterproof design: Fully sealed with M15*12 round hole for installation and a default lead length of 0.5 meters
Application Range:
T30 Liquid Level Detection Sensor can be used for various electrical products, such as water dispensers, water purifiers, air conditioning fans, humidifiers, steam generators and other industrial equipment that require water level control and protection. It is also suitable for detecting liquid levels in different industrial settings.
Design considerations:
When designing the acquisition circuit and software control for the T30 Liquid Level Detection Sensor, it is important to consider the following points:
1. The use of high and low potentials to determine the liquid level is not sufficient.
2. A typical example is the MCU’s I/O port where voltage above 0.7VDD indicates high potential while voltage less than 0.3VDD indicates low potential; any voltage between 0.3VDD and


























There are no reviews yet.